lv obliteration|Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Left Ventricular Cavity : 2024-10-03 Left ventricular (LV) function is determined by the complex interactions between myocardial tissue architecture, myocardial contractility, and loading conditions.
Formuojame žemės ūkį vardan ūkininkų, vartotojų ir mūsų planetos. Niekada dar nebuvo tokio svarbaus meto žemės ūkio inovacijoms. Mūsų pasauliui kyla didžiulių iššūkių - nuo besikeičiančio klimato, ribotų gamtinių išteklių iki augančio gyventojų skaičiaus. Ir mes tikime, kad žemės ūkis yra sprendimo dalis .
0 · Twist Mechanics of the Left Ventricle
1 · Progressive Hypertension and Severe Left Ventricular Outflow Tract
2 · Progressive Hypertension and Severe Left Ventricular Outflow
3 · Left ventricular cavity obliteration: Mechanism of the intracavitary
4 · Left ventricular cavity obliteration: Mechanism of the intracavitary
5 · Left ventricular cavity obliteration: Mechanism of the
6 · Diagnostic and prognostic implications of left ventricular cavity
7 · Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Left Ventricular Cavity
8 · Clinical correlates of left ventricular cavity obliteration
9 · Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: The Variant Less Known
10 · Apical Cavity Obliteration in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Item Data: Crazy Armor Image Name - Game Type - Users Description Attributes / Consume Statistics / Sell Found Notes Galtite - Curse of Darkness Material - Hector A heavy red metal in many layers. Said to draw out a human's latent power, but who really knows? Sell: $50: Steal: Crazy Armor Lv.9, Red Ogre Lv.25/48/75: Evolve: Force .
lv obliteration*******Left ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO), defined as obliteration of the apex in systole on angiography, was first described 1 in 1965 and proposed as the cause of the intraventricular pressure gradient accompanying hypertrophicLeft ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO) was first described as the cause of the gradient but subsequently systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve has .Left ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO) was first described as the cause of the gradient but subsequently systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve has been established as .
Left ventricular cavity obliteration is an angiographic phenomenon in which apical intracavitary space becomes totally occupied in systole by the contracting left .Two‐dimensional strain or speckle tracking demonstrate regional apical dyskinesis and reduced LV “twist,” which can be attributable to cavity obliteration negating the effect of .Left ventricular (LV) function is determined by the complex interactions between myocardial tissue architecture, myocardial contractility, and loading conditions.lv obliterationThese accentuate the problem, leading to impaired diastolic filling, LVOT obstruction, and near obliteration of the LV cavity. The systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve, which .Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Left Ventricular Cavity These accentuate the problem, leading to impaired diastolic filling, LVOT obstruction, and near obliteration of the LV cavity. The systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve, which .Among patients with apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), is apical left ventricular (LV) cavity obliteration associated with an adverse clinical course?Left ventricular (LV) cavity obliteration during dobutamine echocardiography (DE) indicates a vigorous inotropic response to stress. Such a response may suggest the absence of .Left ventricular (LV) cavity obliteration during dobutamine echocardiography (DE) indicates a vigorous inotropic response to stress. Such a response may suggest the . Left ventricular cavity obliteration is an angiographic phenomenon in which apical intracavitary space becomes totally occupied in systole by the contracting left ventricular muscle. To determine the clinical associations and physiologic significance of this finding we reviewed the clinical, echocardiographic, hemodynamic and angiographic .The diagnostic features of left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) were characterized >50 years ago.1-3 In contrast, the features of mid-cavitary obstruction (MCO) at cardiac . Left ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO) was first described as the cause of the gradient but subsequently systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve has been established as the cause. .
Objective Apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is characterised by apical systolic obliteration and is associated with atrial fibrillation (AF), stroke, heart failure (HF), and mortality. We investigated whether apical obliteration of the left ventricular (LV) cavity could have an unfavourable impact on the clinical course of apical HCM. Methods 188 .
Although obliteration of the left ventricular (LV) cavity at end-systole is interpreted as indicative of intraoperative hypovolemia, this relation has not been demonstrated directly. Methods: We continuously monitored the LV short axis by using transesophageal echocardiography and determined the relation between acute changes in LV area and . Left ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO) was first described as the cause of the gradient but subsequently systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve has been established as the cause .
The Henry Ford Health Scholarly Commons is a collection of medical journals and scholarly articles.LV cavity demonstrated on apical 4-chamber views. In all patients, cavity obliteration was defined as obliteration of the LV apical cap with variable extension into the mid-LV cavity. Of these 65 patients, 49 were inpatients, 17 were on intravenous inotropes, and 5 patients had sepsis; there were a variety of other diagno - Even after exclusion of patients with LV dysfunction, cavity obliteration was an independent predictor of freedom from events (RR 0.41, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.88, p = 0.02). Thus, LV cavity obliteration is a frequent response to DE, which compromises the sensitivity of DE but is correlated paradoxically with a favorable clinical outcome.
1 INTRODUCTION. Left ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO), defined as obliteration of the apex in systole on angiography, was first described 1 in 1965 and proposed as the cause of the intraventricular pressure gradient accompanying hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. It was subsequently documented 2 that cavity obliteration can be .
Echocardiography revealed severe left ventricular hypertrophy, hyperdynamic left ventricular (LV) function, mid-cavity obliteration of the LV in systole, and a small localized apical aneurysm. Doppler echocardiography showed a mid-cavity gradient of 36 mm Hg without any LV outflow tract gradient. In addition, Doppler echocardiography revealed . Introduction. A left ventricular outflow tract pressure gradient (LVOT PG) ≥50 mmHg at rest in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a predictor of heart failure and cardiovascular death [1, 2].The clinical indication for myectomy and alcohol septal ablation is also LVOT PG ≥50 mmHg at rest or with physiological exercise [].We also encounter .Left ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO) was rst described as the cause of the gradient but subsequently systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve has been established as the cause. Nevertheless, the two gradients, though di erent in origin and signi cance, share similar characteristics. They both have a similar \dagger" pro le, are . Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) refers to the limitation of blood flow out of the left ventricle. The level of obstruction can be valvular, sub-valvular, or supravalvular. It can include anatomic stenotic lesions anywhere from left ventricle (LV) outflow to descending aorta. Hemodynamically, LVOTO has been defined as a peak .Echocardiography revealed severe left ventricular hypertrophy, hyperdynamic left ventricular (LV) function, mid-cavity obliteration of the LV in systole, and a small localized apical aneurysm. Doppler echocardiography showed a mid-cavity gradient of 36 mm Hg without any LV outflow tract gradient. In addition, Doppler echocardiography revealed . Introduction. A left ventricular outflow tract pressure gradient (LVOT PG) ≥50 mmHg at rest in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a predictor of heart failure and cardiovascular death [1, 2].The clinical indication for myectomy and alcohol septal ablation is also LVOT PG ≥50 mmHg at rest or with physiological exercise [].We also encounter .Left ventricular cavity obliteration (LVCO) was rst described as the cause of the gradient but subsequently systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve has been established as the cause. Nevertheless, the two gradients, though di erent in origin and signi cance, share similar characteristics. They both have a similar \dagger" pro le, are . Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) refers to the limitation of blood flow out of the left ventricle. The level of obstruction can be valvular, sub-valvular, or supravalvular. It can include anatomic stenotic lesions anywhere from left ventricle (LV) outflow to descending aorta. Hemodynamically, LVOTO has been defined as a peak . The preload is completed at this point. The diastolic gradients in the left ventricle occur between the left ventricle base near the mitral valve and the apex and between the apical zone and the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) . These diastolic gradients seem to have an important role in left ventricular (LV) filling and emptying . In .
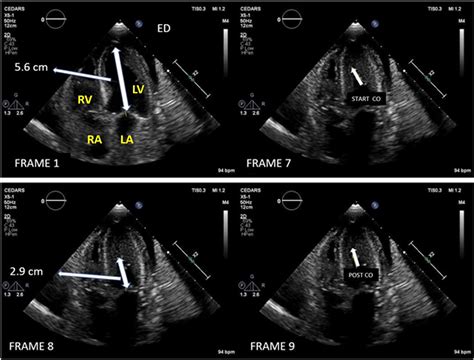
More subjective criteria for the diagnosis of AHC include: obliteration of the LV apical cavity in systole, failure to identify a normal progressive reduction in LV wall thickness towards the apex and apical aneurysm formation with delayed enhancement [25, 26]. The formation of apical aneurysm is thought to be due to ischaemia, which results .

In this issue of Circulation Cardiovascular Imaging, Sabatino et al 15 reported the added clinical value of LV twist measurement to differentiate LV noncompaction, diagnosed using cardiac magnetic resonance, from the hypertrabeculated left ventricle in children (LV twist angle cutoff value <5.8°; sensitivity, 82%; specificity, 92%; AUC=0.914).
In such settings, endocardial excursion and thickening of the LV is increased, leading to near or actual end-systolic obliteration of the LV cavity ( Figure 14.4 and Video 14.2). Although a hyperdynamic LV frequently suggests hypovolemia and/or vasodilation, other etiologies that can severely decrease preload or afterload should be .
Left ventricular cavity obliteration Is an angiographic phenomenon in which apical Intracavltary space becomes totally occupied In systole by the contracting left ventricular muscle. To determine the clinical asso-ciations and physiologic significance of this finding we reviewed the clinical, echocardiographic, hemodynamic and angiographic data . Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most common inherited cardiac disease, with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 500 in the adult population. 1–3 Pathogenic variants in genes that encode cardiac sarcomeric proteins are responsible for causing disease in roughly 60% of familial and 20% to 30% of apparently sporadic HCM. 4 Left . This also implies that patients with smaller left ventricular cavities will more quickly develop a increased contractility-induced cavity obliteration. In resting patients, the stroke volume reducing effect of a smaller ventricular cavity appears to be compensated by an increase in resting heart rate but functions to reduce cardiac reserve .
Your home is 300% more likely to be robbed with no home security system. Crime Grade's crime map shows the safest places in 89121 in green. The most dangerous areas in 89121 are in red, with moderately safe areas in yellow. Crime rates on the map are weighted by the type and severity of the crime.
lv obliteration|Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Left Ventricular Cavity











